At the heart of creating websites lies HTML, Hypertext Markup Language. A well-structured HTML document follows a specific hierarchy of elements, ensuring clarity and accessibility for both users and search engines alike. Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental components of an HTML page, presented with clear explanations and examples.
DOCTYPE Declaration
<!DOCTYPE html>This declaration tells browsers what version of HTML you’re using in our case, HTML5. It helps ensure consistent rendering across different devices and browsers.
Root Element
<html></html>The <html> tag serves as the root element, containing everything else on your page.
Head Section
<head></head>Within the head section, you can place information such as titles, meta descriptions, character encoding, and links to stylesheets and scripts.
For Example
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>My First Website</title>
</head>Title Tag
<title></title>The <title> tag determines the title that displays in the browser’s title bar or tab.
Body Tag
<body></body>The <body> tag holds the actual content of your webpage, including text, images, videos, etc..
A common example of an HTML page appears as follows
Content Examples
Here’s a simple HTML file demonstrating some common elements
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>My First Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Site!</h1>
<p>I hope you enjoy your visit here.</p>
</body>
</html>The image below offers a visual representation of the structure of HTML
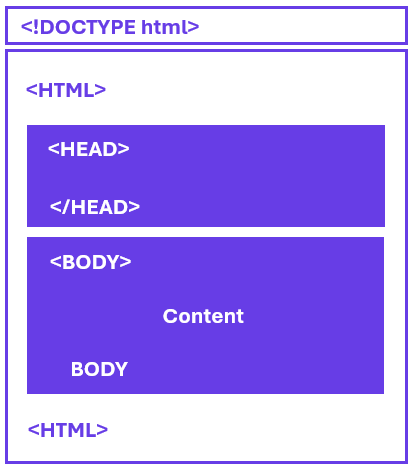
Summary
<!DOCTYPE html>specifies the HTML version.<html>wraps around all content.<head>contains metadata.<title>sets the webpage title.<body>holds the visible content.
By understanding these basic elements, you can create and structure HTML pages effectively. In future tutorials, we’ll explore more HTML tags and elements.